The Earth is technically located within the Sun's atmosphere: how is that possible?
It may seem strange that Earth is technically located within the Sun's atmosphere. However, this is indeed the case, and in the future, our planet may move beyond this atmosphere, as reported by IFLScience.
The Sun is one of the hundreds of billions of stars in the Milky Way galaxy, and it is not the most common type of such astronomical objects. The Sun is approximately 150 million km away from Earth and, like many other stars, it is a sphere of very hot plasma. The temperature on the surface of the Sun is hundreds of times lower than the temperature in its outermost layers. In any case, studying the internal structure of the Sun is a very complex task.
Scientists study the internal structure of the Earth using seismic waves that travel through the planet's interior. In a similar manner, researchers observe the waves passing through the Sun and their impact on electromagnetic waves at the surface of our star to gain a better understanding of its internal structure.
According to Stephen Serjeant from The Open University in the UK, sound waves travel through the Sun and reach its surface. Thus, when observing our star with the SOHO spacecraft, the waves stretch and compress, creating the illusion that the surface of the Sun is moving toward or away from the spacecraft.
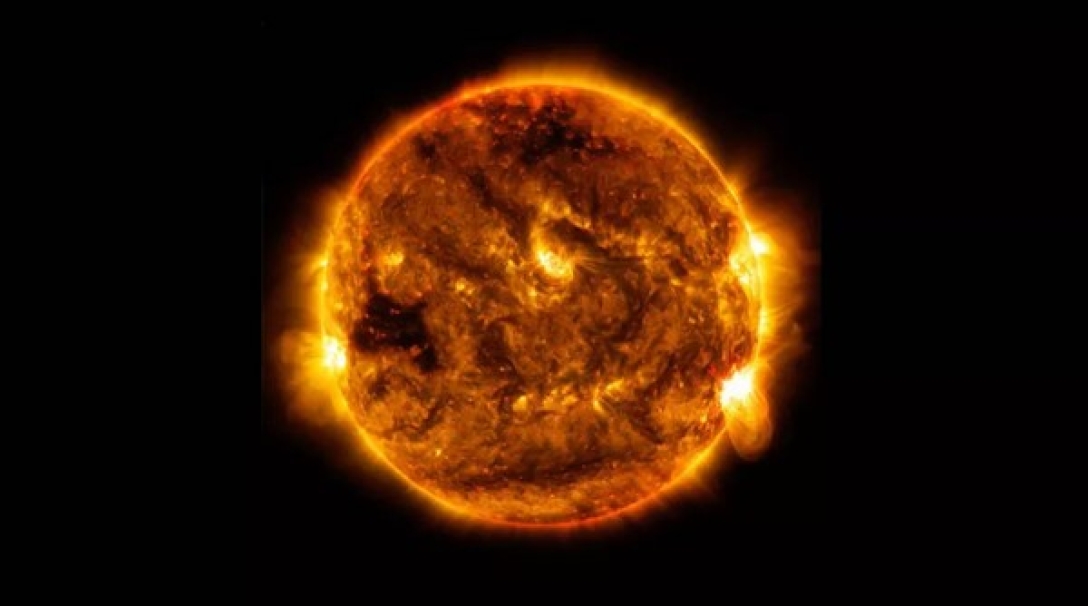

The surface of the Sun also emits light, and light waves are compressed or stretched. The SOHO spacecraft measures the change in the wavelength of light, and then scientists translate this into information about the sound waves that have reached the surface of our star.
Using this and other methods, scientists have determined that the Sun has a core that rotates four times faster than the surface of the star. The core, where nuclear fusion occurs and hydrogen is converted into helium, is surrounded by a radiation zone, above which lies the convection zone, followed by the chromosphere, and the outermost layer of the Sun's atmosphere is the corona. However, the atmosphere of the Sun does not end here.
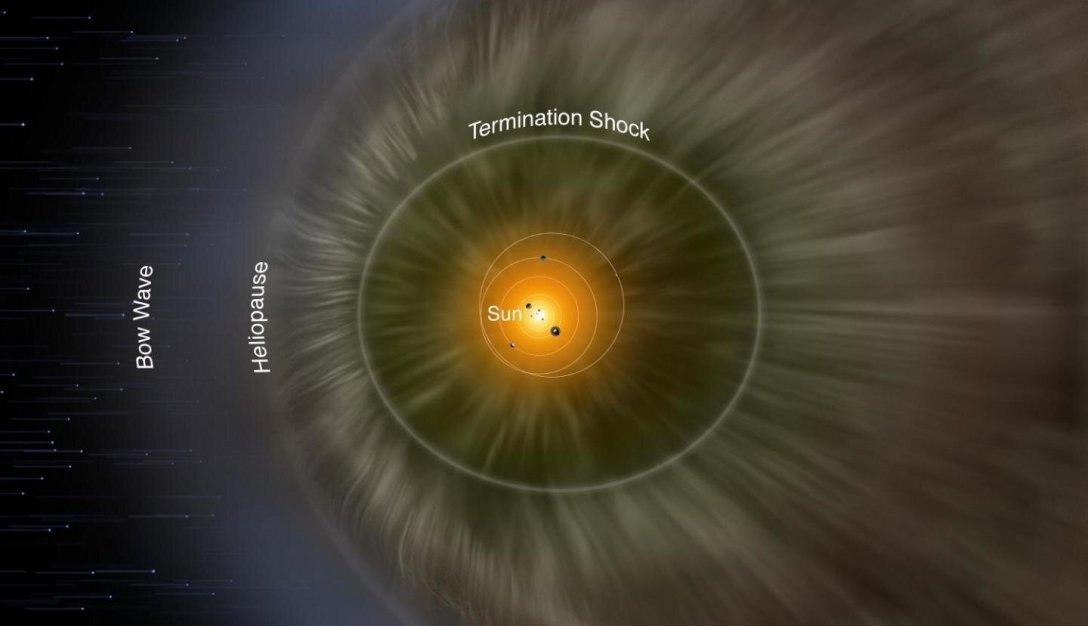
Once plasma leaves the solar corona at supersonic speeds, it transforms into solar wind, which creates the heliosphere. This is the region of space where the gravity of our star and the influence of its magnetic field extend.
The heliosphere stretches far beyond the orbit of the farthest planet in the Solar System—Neptune. Thus, Earth is located within the Sun's atmosphere, while interstellar space lies beyond the heliosphere. The heliosphere protects Earth from the negative effects of the interstellar medium.
Recent research has shown that the heliosphere may have contracted when the Solar System passed through a cold gas cloud several million years ago. This affected the climate of our planet. Scientists believe that the contraction of the heliosphere lasted for tens or even hundreds of thousands of years, and there is a possibility that the Solar System will pass through a cold gas cloud again within the next million years, leading to a new contraction of the heliosphere.
Researchers believe that during the contraction of the heliosphere, changes in the Earth's climate occurred, which could have influenced human evolution. It is suggested that the emergence of Homo sapiens was driven by the need to adapt to new conditions on our planet. The fact is that when the heliosphere contracted, Earth became directly exposed to the influence of the interstellar medium.